Published: October 4, 2023
Emerging Cybersecurity Threats: What Professionals Need to Know
By TalPoint Marketing articles
In the evolving digital landscape, cybersecurity remains a persistent challenge. As technology becomes more sophisticated, so do the threats that organizations face. This article examines some of the current and emerging cybersecurity threats professionals need to be aware of.
Supply Chain Compromise
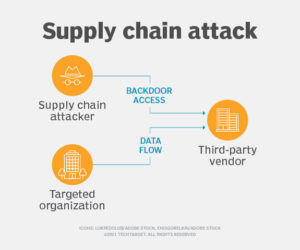
Recent years have seen a sharp increase in software supply chain attacks, representing a serious risk to organizations worldwide. High-profile incidents such as SolarWinds, Equifax, and Target illustrate the evolving threat landscape, with a study by KPMG disclosing that 73% of organizations have faced at least one significant disruption from a third party in the last three years. These attacks are emerging as substantial threats where adversaries manipulate legitimate software to infiltrate target systems. Understanding the intricate nature of software dependencies is essential to bar unauthorized access and uphold system integrity. Proactive and ongoing monitoring, assessment, and updating of software components are critical, serving as a shield against the risks linked to supply chain attacks and fortifying defenses to ensure a robust and secure operational environment.
IoT Attacks
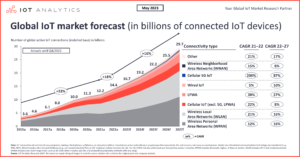
In 2023, it’s projected that the global number of connected IoT devices will surge by 16%, amounting to 16.7 billion active endpoints. By 2025, this figure is anticipated to soar to an astounding 30.9 billion. As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues its expansive growth, the potential attack surface for cybercriminals correspondingly expands. Many IoT devices remain susceptible to network breaches, including data theft, phishing attempts, spoofing, and debilitating denial of service attacks (DDoS). Such vulnerabilities can pave the way for more severe cybersecurity threats, such as ransomware onslaughts and impactful data breaches. The repercussions of these breaches often result in substantial financial and reputational costs for businesses. The pervasive presence of IoT underscores the need for rigorous security protocols. Implementing these safeguards is vital to shield sensitive data and block unauthorized access. Measures like secure communication protocols and consistent firmware updates can significantly curtail the risks associated with IoT devices.
Human Error

Human error is the culprit in nearly 90% of cyber incidents, underlining the critical role of human vulnerability in cybersecurity. Studies consistently reveal that inadvertent mistakes by users and inadequate awareness of cybersecurity practices often lead to severe breaches, highlighting the critical role of the human element in organizational security. Minor missteps, such as using insecure passwords or clicking on malicious links, can expose organizations to significant risks, jeopardizing sensitive data and business operations.
Addressing human error requires a twofold strategy: limiting opportunities for mistakes and enhancing user education. However, the prevalent approach to cybersecurity education in many organizations—initial training followed by infrequent refreshers—is inadequate. Persistent and evolving education is crucial to equip employees with the knowledge and skills needed to navigate the ever-changing landscape of cyber threats effectively.
Cloud Vulnerabilities

The rapid shift towards cloud computing has uncovered a range of vulnerabilities, leading to significant cybersecurity challenges. Current projections suggest that by 2025, over 95% of new digital workloads will run on cloud-native platforms, a substantial jump from just 30% in 2021. The appeal is clear: businesses are drawn to the cloud for its flexibility and the convenience of accessing data from any device, anytime, anywhere. While the cloud offers agility and scalability, it’s not without its security pitfalls. A recent report highlights this tension, with 76% of organizations expressing concern about their cloud security, and nearly a quarter admitting they faced a cloud security incident in the past year.
Persistent issues like misconfigurations and weak access controls often lead to data leaks and breaches. As businesses increasingly adopt multi-cloud and hybrid-cloud solutions to improve performance and efficiency, maintaining consistent security measures across various platforms is crucial. There’s also a rising emphasis on the zero-trust security model within cloud settings: a “trust no one, verify everyone” approach. This shift means that businesses are moving towards a more comprehensive and layered strategy to protect their digital assets in this ever-evolving landscape.
For organizations making the move to the cloud, the risks are real and growing. Ensuring proper setups, strong access protocols, and regular security checks are essential to keeping cloud data safe. Investing time and resources into cloud security best practices is not just recommended, but imperative to fend off looming threats.
Skills Shortage
The cybersecurity skills gap is a pressing concern, with organizations struggling to find qualified professionals to safeguard against sophisticated threats. The industry is grappling with a talent shortage, revealing that 63% of respondent organizations have unfilled cybersecurity positions and 60% experiencing difficulties retaining qualified cybersecurity personnel. Between 2013 and 2021, the number of unfilled cybersecurity jobs grew from 1 million to 3.5 million – a 350% jump. The same number of openings will still be available in 2025 according to some. Others believe that the gap will widen even further with the demand for certain cybersecurity practitioners increasing faster than supply can keep up. For instance, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts that the demand for information security analysts will grow by 35% between 2021 and 2031, much faster than the average for all occupations.
So what can organizations do? Many companies are scaling up their efforts to tackle the cybersecurity skills shortage. Some are working with staffing and recruitment agencies, while others are partnering with certification organizations, schools, universities, and government workforce programs. Many larger companies are also leading efforts to grow the global cybersecurity workforce. For example, Microsoft launched a campaign to expand the U.S. cybersecurity workforce by 2025. Search engine giant Google has pledged to teach 100,000 Americans in-demand skills like data privacy and security through the Google Career Certificate program. IBM has also announced its intentions to train 150,000 people in cybersecurity skills by 2024.
Another increasingly-popular avenue is to sign up on talent marketplaces like TalPoint that enable companies of all sizes to source experts in security, privacy, risk and compliance. Talent marketplaces offer a robust, efficient, and innovative solution to the modern-day talent conundrum. Companies that harness their potential today will be better poised for success in the ever-evolving landscape of tomorrow.
Learn more about the talent shortage root causes and strategies to attract talent here.
Ransomware and Phishing

In recent years, phishing and ransomware have become top cybercrimes, posing a growing threat to many businesses. In 2022 alone, there were over 300,000 complaints about phishing. Most businesses have faced these types of attacks. The rising number of these attacks shows the urgent need for better cybersecurity knowledge and strong security systems. It’s vital to teach employees how to spot phishing attempts and to keep data and systems safe.
To defend against ransomware:
- Keep your software and OS up to date.
- Train users about the dangers of unknown links and attachments.
- If you use RDP, make sure it’s safe and watched.
- Backup your data offline.
To defend against phishing:
- Teach users to identify phishing attempts (but be cautious with fake phishing tests).
- Require multi-step password verification.
- Ask users to report suspicious emails.
- Set clear rules for urgent & last minute requests.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Abuse
The growth of cybercrime is largely due to the easier access and reduced barriers for malicious actors. Cybercriminals are adapting by offering subscription services and starter kits, and even potentially using large language models like ChatGPT for nefarious purposes. As a result, business leaders must be up-to-date with AI’s role in cybersecurity. Some key points to consider:
- Evolution of Cybercrime-as-a-Service: Modern cybercriminals are commoditizing their expertise, offering subscription models and kits, which facilitate entry for novice adversaries.
- AI’s Growing Role in Cybersecurity: A notable 63% of corporate executives report an increased expenditure on AI-driven solutions. This shift predominantly stems from the vast volumes of data generated, which is beyond manual human analysis.
- Anticipated Investments in AI-Powered Cybersecurity: Research conducted by Blackberry found that 82% of IT decision-makers intend to allocate resources to AI-centric cybersecurity within the next two years, with approximately half poised to invest by the conclusion of 2023.
- Potential Misapplication of AI: While tools such as ChatGPT can potentially be commandeered to craft intricate attacks, it’s essential to understand that these tools are not standalone threats. They necessitate human oversight and are not entirely autonomous in malicious endeavors.
However, it’s vital to underscore that AI’s intersection with cybersecurity isn’t solely a threat vector:
- Proactive Safeguarding: AI-driven systems have the capability to discern patterns, enabling automated incident responses, thus bolstering cybersecurity measures.
- Real-time Surveillance: Advanced AI mechanisms can instantly identify security breaches, aiding human cybersecurity experts in threat recognition.
- Efficiency Enhancement for Analysts: AI streamlines various tasks like network monitoring, effectively distinguishing genuine threats from benign anomalies.
- Amplified Access Security: AI’s analytical abilities can enhance security by detecting anomalies, spotlighting suspicious login activities, and championing the implementation of robust authentication methods.
- Mitigation of Internal Threats: AI’s ability to monitor user patterns allows for early detection and prevention of potential security breaches from within an organization.
While business leaders must be cognizant of the potential risks AI introduces to cybersecurity, it is equally imperative to recognize and harness its capabilities as a potent defensive tool. The dual-faceted role of AI in cybersecurity mandates a balanced approach, ensuring that its advantages are leveraged while its potential misuses are stringently mitigated.
Poor Data Management
By 2025, experts anticipate the global datasphere to surge to a colossal 163 zettabytes. Alarmingly, while nearly 90% of this data will demand some form of security, less than half will actually be safeguarded. This underlines the precarious state of cybersecurity, particularly with businesses facing grave consequences for lax data management. For instance, in May 2023, Meta faced a jaw-dropping fine of $1.3 billion after an Irish court decreed they breached GDPR laws, specifically regarding data transfers between the E.U. and the U.S. Furthermore, the data breach’s average global cost soared to $4.45 million in 2023, marking a 15% surge over just three years. With the average company sitting on a staggering 534,465 files teeming with sensitive information, the dangers of mishandling data become crystal clear. Non-compliance to data protection norms doesn’t just heighten breach vulnerabilities; it also brings along hefty penalties. It’s concerning to note that a whopping 70% of compliance professionals cite keeping abreast with the ever-evolving regulatory landscape as their foremost challenge. Amidst these concerns, issues of data integrity loom large, casting shadows on essential decisions and processes.
In today’s data-driven world, the manner in which organizations handle and protect their data is paramount. Poor data management practices can leave gaping vulnerabilities in the system, subjecting companies to substantial risks. These risks aren’t merely technical; they resonate deeply on financial, reputational, and operational fronts. Data breaches, which are becoming alarmingly common, can leak confidential client information, causing irreparable harm to brand trust. Furthermore, the loss of intellectual property, a company’s treasured asset, can result in lost competitive advantages and major economic setbacks.
However, these pitfalls can be averted. Implementing robust data governance frameworks is a game-changer. Such frameworks ensure standardized procedures, clear accountabilities, and systematic monitoring of data assets. By fostering a culture that emphasizes the importance of data protection and by adopting industry best practices in data management, organizations can not only safeguard their sensitive information but also enhance their operational efficiencies. In a landscape where data is the new gold, maintaining its sanctity and security is crucial for organizational resilience, growth, and long-term success.
Conclusion
Emerging cybersecurity threats are reshaping the way professionals approach digital security. It is pivotal for organizations and cybersecurity professionals to stay abreast of these evolving threats and implement comprehensive security measures to safeguard against them. By fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness, investing in advanced security solutions, and promoting ethical technological practices, we can navigate the complex landscape of new-age vulnerabilities and ensure a secure digital future.
Discover how our services can offer your organization the perfect solution to your cybersecurity needs. Click here to learn more!




